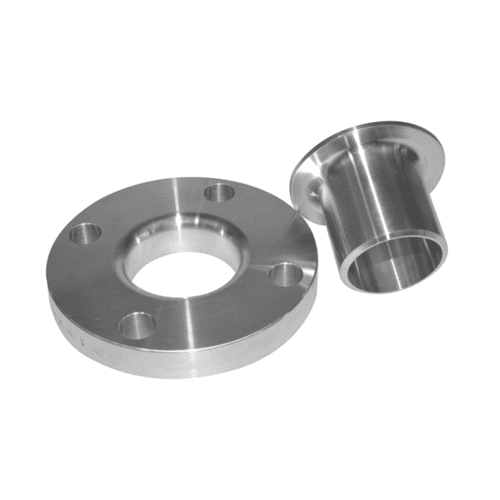
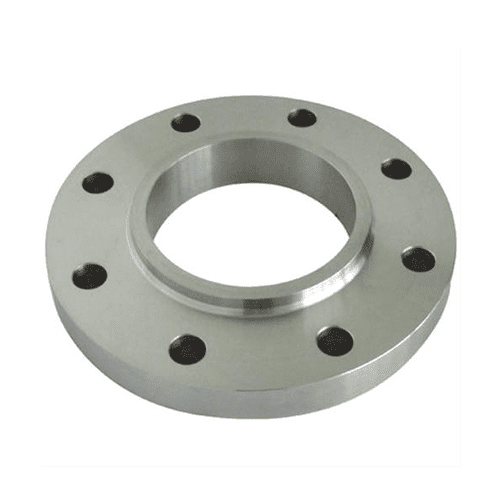
Lap Joint Flange
The [Lap Joint Flange] is one such important accessory used for joining the pipes and fittings within a wide variety of piping systems. The design of this flange is such that it is capable of working with a stub end as a solution for easy quick joining or separation. Important industries in which this flange is widely used include oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment.
Material Specifications
We offer [Lap Joint Flanges], made from high-quality materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel, to have adequate strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. The [Lap Joint Flange] is widely valued for being compatible with misalignment in the piping system, and so it is advocated for use in large industrial needs.
Technical Specifications
The [Lap Joint Flanges] are manufactured in sizes from as low as 1/2 inches all the way up to 48 inches, thus meeting even the demands of the extensive pipeline. They can withstand pressures of 1500 PSI and temperatures that range from -20°C up to 400°C. Common dimensions include the [Lap Joint Flange Dimensions 150], which are designed to offer quality performance under various operational contexts.
Standards and Compliance
The flanges of the pipes are, on the other part, manufactured following international standards such as ASTM, ASME and ISO 9001. As the prime suppliers of such lapped joint flanges, we promise to make things right for our products to undergo stringent testing in line with such standards. The assurance provided to customers is that of safety, reliability, and performance. Certification from a lapped-joint flange supplier confirms adherence to quality management and excellence in customer service.
Usage Instructions
Regular maintenance, including inspection and cleaning, is recommended to make the most out of your [Lap Joint Flange] in terms of performance and long life. Measures to ensure appropriate specification at installation Countermeasures are mostly linked with installation. For detailed options in troubleshooting and the correct information when it comes to maintenance, read on in the user handbook, or reach us directly through our technical support team.
Applications
The [Lap Joint Flange] is a critical importance to most systems since a tight connection eliminates leakage. Flange usage can be found in oil and gas pipeline lines, chemical processing, and various water treatment facilities. It is helpful to ensure that proper [Lap Joint Flange Dimensions 150] get configured so that systems’ integrity, when in use, will be leak-tight under the intended maximum working pressure conditions.
This will be particularly useful in the HVAC systems, where the connections are reliable and no single leaks could be tolerated in these pipelines. Because of its robust design and different materials it could come in, it will therefore ensure reliability and durability in a number of environments. The [Lap Joint Flange Dimensions 150] are of a preference in dealing with larger diameter pipes, thus making them effective for use in most heavy-duty industrial setups.
This [Lap Joint Flange] is designed for highly effective and simple connecting under high-pressure conditions. The solid mechanism ensures durability and reliability—just perfect for a very harsh and challenging environment. The [Lap Joint Flange Suppliers] produce huge varieties of lap joint flanges, including completely different customized solutions to meet individual industrial requirements. It is these levels of adaptabilities that make them the most preferred suppliers for projects that need preciseness in engineering and reliability.
Features and Benefits
Features:
- Uses advanced technology for sealing, which ensures a tight closure with no leaks.
- Because of this, the [Lap Joint Flange] is said to be designed for easy assembling and disassembling of a system that typically requires maintenance.
- The ease of installation and maintenance of a lap joint flange brings a versatile design, which in turn reduces downtime and associated labor costs.
Benefits:
- Its long service life and reduced maintenance requirements are ensured by both the use of highly durable construction materials and design features.
- The [Lap Joint Flange] serves of tremendous help in leak avoidance, ensures high reliability with minimized downtime, and thus protects critical equipment from damage.
- By being cost-effective from [Lap Joint Flange Suppliers], it is competitive, and as such, it will provide cost-effective flanges for many businesses in both quality and quantity.
Related Products
To ensure comprehensive system protection and efficiency, consider integrating these related products:
- [Gate Valves]: Provides robust shutoff capabilities for high-pressure environments.
- [Globe Valves]: Provides accurate throttling and flow regulation, supplementing secure connection functionalities of lap joint flanges.
- [Strainers]: Protect lap joint flanges from debris and sediments, extending their service life while maintaining flow efficiency at high levels.
Call to Action
“Request a Quote” for bulk pricing, or “Contact Us for More Information” for customized solutions. Our expert team from [Lap Joint Flange Suppliers] is ready to assist you in selecting the ideal flange to meet your specific needs.
Support and Warranty Information
Our [Lap Joint Flanges], including the [Lap Joint Flange Dimensions 150], are backed by a comprehensive warranty and full-scale customer support by the trusted [Lap Joint Flange Suppliers]. We provide ease of installation, operation support, and troubleshooting services to ensure your flange performs optimally over its service life.